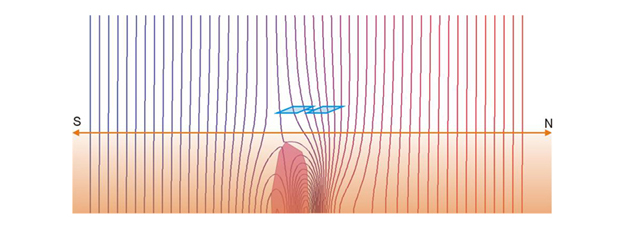
What does gradient tensor of the Earth magnetic field mean?
The gradient tensor is a mathematically exact description of the change rate of the earth magnetic field.
On the basis of the Maxwell equations electrodynamics; the gradient tensor is described by five independent components, three non-diagonal elements and two diagonal elements of the tensor matrix.
The availability of gradient tensor data can be seen as a quantum leap in airborne geomagnetics as it provides plenty of completely new information:
- continuous mapping of the magnetisation direction of the rocks,
- continuous mapping of the remanence indicators,
- Mapping of the magnetic susceptibility,
- continuous three-dimensional determination of rock properties,
- Recording of geologic peripheral zones,
- Improvement of the resolution of the total field measurements using field gradients contained in the tensor data.
Measuring principle
The change of the homogeneity of the earth magnetic field caused by concealed magnetic materials is detected by JESSY STAR. Gradiometer sensors allow an extraordinary good localization of those materials.